Image Source: Google
Climate change is one of the most pressing issues facing our planet today. The increase in greenhouse gas emissions, particularly carbon dioxide (CO2), is contributing to rising global temperatures and extreme weather events. In the fight against climate change, carbon capture and storage (CCS) has emerged as a promising technology that could help reduce CO2 emissions and mitigate the impact of climate change.
The Basics of Carbon Capture and Storage
Carbon capture and storage is a process that involves capturing carbon dioxide emissions from sources such as power plants and industrial facilities, transporting it to a storage site, and storing it underground to prevent it from entering the atmosphere. The three main steps involved in CCS are:
1. Capture:
- CO2 is captured from sources such as power plants, cement plants, and refineries before it is released into the atmosphere.
- There are different technologies available for capturing CO2, including pre-combustion capture, post-combustion capture, and oxy-fuel combustion.
2. Transport:
- Once captured, the CO2 is transported via pipelines, ships, or trucks to a storage site.
- The transportation of CO2 is crucial to ensure that it reaches the storage site safely and efficiently.
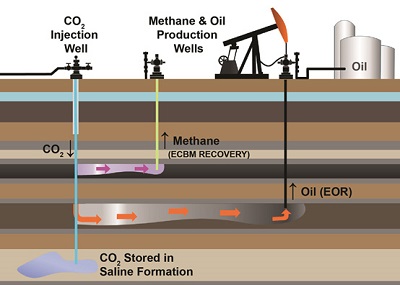
3. Storage:
- At the storage site, the CO2 is injected deep underground into geological formations such as depleted oil and gas reservoirs, saline aquifers, or coal seams.
- The CO2 is stored securely underground to prevent it from escaping back into the atmosphere.
The Benefits of Carbon Capture and Storage
Carbon capture and storage offers several benefits in the fight against climate change:
1. Emissions Reduction:
- CCS can help reduce CO2 emissions from power plants and industrial facilities, which are significant contributors to greenhouse gas emissions.
- By capturing and storing CO2 underground, CCS helps to prevent it from entering the atmosphere and contributing to global warming.
2. Climate Mitigation:
- By reducing CO2 emissions, CCS can help mitigate the impact of climate change and limit global temperature rise.
- It provides a way to decarbonize industries that are difficult to electrify, such as steel and cement production.
3. Energy Security:
- CCS can be integrated with other low-carbon technologies such as renewable energy sources to help ensure energy security while reducing emissions.
- It can also be used in conjunction with bioenergy to achieve negative emissions, where more CO2 is removed from the atmosphere than is emitted.
Challenges and Barriers to Deployment
While carbon capture and storage hold promise as a groundbreaking solution to climate change, there are several challenges and barriers that need to be addressed for widespread deployment:
1. Cost:
- The cost of capturing, transporting, and storing CO2 is currently high, making CCS less economically competitive compared to other technologies.
- Investment and financial incentives are needed to drive down costs and make CCS more viable for industries.
2. Regulation and Policy:
- Regulatory frameworks and policies that support the deployment of CCS are essential to incentivize industries to adopt the technology.
- Clear guidelines on CO2 storage and liability issues need to be established to address concerns about environmental impacts and risks.
3. Public Perception:
- Public acceptance and trust in CCS technology are crucial for its successful deployment.
- Education and awareness campaigns are needed to address misconceptions and build support for CCS projects.
The Future of Carbon Capture and Storage
Despite the challenges, carbon capture and storage have the potential to play a significant role in reducing CO2 emissions and combating climate change. The following developments are shaping the future of CCS:
1. Innovation and Research:
- Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on improving CCS technologies, enhancing efficiency, and reducing costs.
- New advancements in materials science and engineering are driving innovation in CO2 capture and storage techniques.
2. Policy Support:
- Governments and international organizations are increasingly recognizing the importance of CCS in achieving climate goals and are providing incentives and support for CCS projects.
- Policies such as carbon pricing and emission reduction targets are creating a favorable environment for the development of CCS infrastructure.
3. Industry Collaboration:
- Collaboration between industries, research institutions, and governments is essential to overcoming barriers and accelerating the deployment of CCS technology.
- Partnerships and initiatives such as the Carbon Sequestration Leadership Forum (CSLF) are fostering collaboration and knowledge sharing in the CCS community.
Conclusion
Carbon capture and storage have the potential to revolutionize the way we address climate change by reducing CO2 emissions and mitigating the impact of global warming. While there are challenges to overcome, continued innovation, policy support, and industry collaboration are key to unlocking the full potential of CCS as a groundbreaking solution to climate change.
